Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124


This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, we may earn commissions from qualifying purchases.
Have you ever considered the incredible ways in which land drones are being utilized across various industries? These fascinating machines, also known as unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs), have moved far beyond their military origins and are now transforming our daily lives. From agriculture to disaster response, the uses of land drones are vast and varied.
Land drones are autonomous or remotely operated vehicles that traverse terrestrial landscapes. Unlike aerial drones or marine drones, land drones are designed to operate on the ground, providing solutions in scenarios where conventional human intervention is impossible, inefficient, or hazardous. They come in various sizes and capabilities, ranging from small robots used in homes to large, rugged machines built for industrial purposes.
To understand their uses, it’s essential to grasp the core components of land drones:
Now that you have a basic understanding of what makes up a land drone, let’s examine their primary uses.
The military was among the first sectors to adopt land drones. Their ability to operate in hostile and dangerous environments makes them invaluable in various defense scenarios.
Land drones equipped with high-definition cameras and sensors can gather intelligence without putting soldiers in harm’s way. These drones can navigate through rough terrains, providing real-time data to military personnel about enemy positions, fortifications, and other tactical information.
Land drones play a critical role in bomb disposal units. Equipped with manipulator arms and specialized cameras, they can safely disarm explosive devices. They are also used in mine detection, using ground-penetrating radar and other sensors to locate hidden mines.
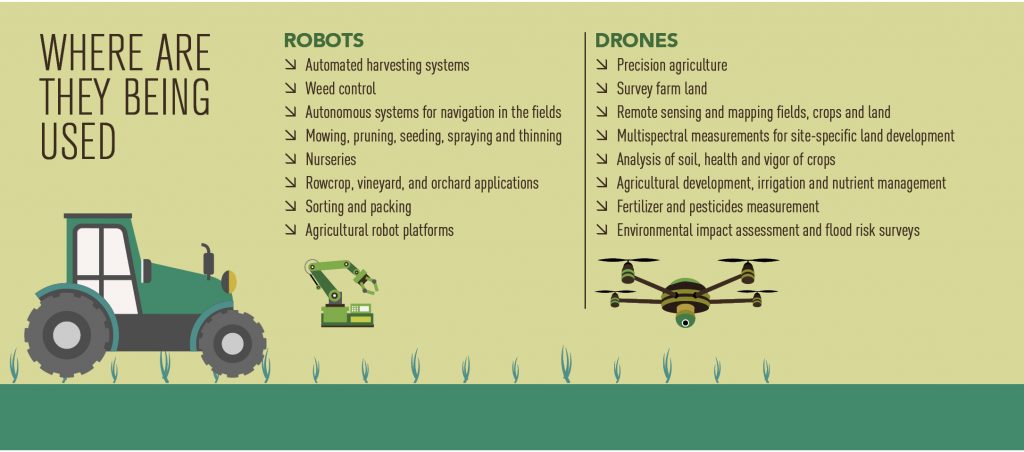
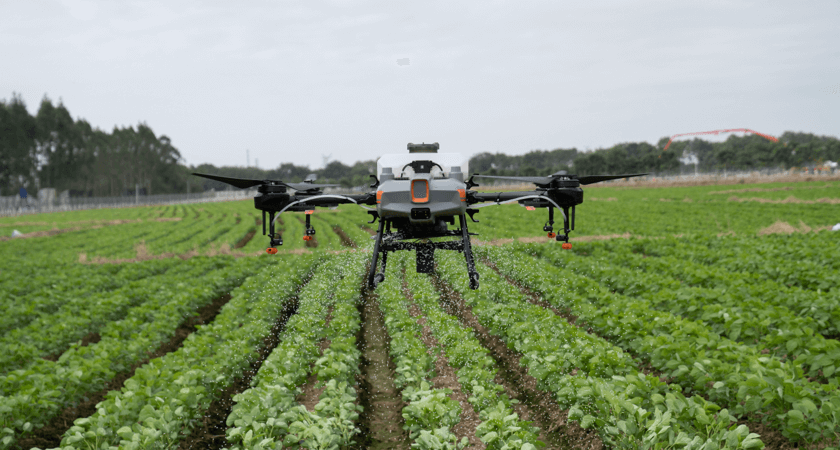
Modern agriculture has seen a significant influx of technology, and land drones are at the forefront of this revolution.
Land drones equipped with multispectral cameras can assess crop health by analyzing various wavelengths of light. This helps farmers detect issues such as pest infestations and nutrient deficiencies early, enabling timely interventions.
Land drones are used for precise planting, fertilizing, and pesticide application. They help in evenly distributing resources, thereby increasing crop yields and reducing waste. Autonomous tractors have also become crucial tools in large-scale farming, performing tasks with high precision.
In the aftermath of natural disasters, the first few hours are crucial for rescuing survivors and assessing damage. Land drones can significantly enhance these efforts.
Equipped with thermal imaging cameras, land drones can locate survivors trapped under rubble or debris. They can navigate through confined spaces that are challenging for human rescuers to access, making them invaluable in search and rescue missions.
Land drones can quickly survey disaster-stricken areas, providing real-time visual data to emergency response teams. This rapid assessment helps in deploying resources efficiently and formulating effective response strategies.
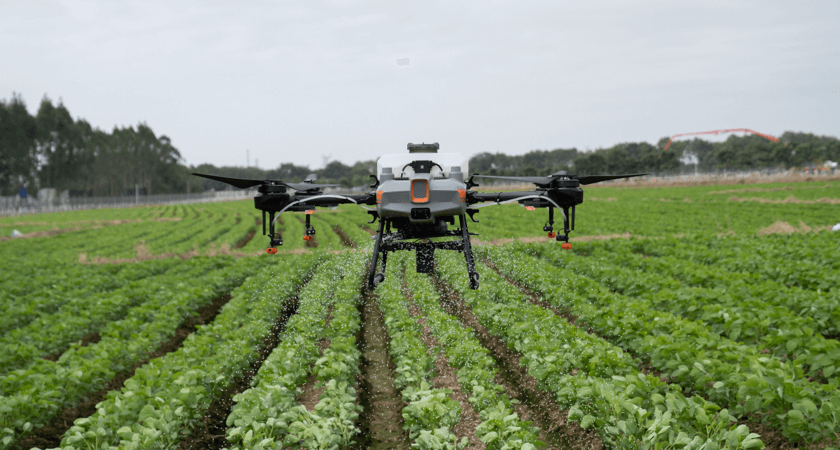

The industrial sector has also embraced land drones for their efficiency and ability to perform in hazardous environments.
In large warehouses, land drones are used for inventory management, picking, and sorting tasks. These drones can operate autonomously, significantly increasing the efficiency of warehouse operations and reducing the need for human labor in repetitive tasks.
Industries such as oil and gas, mining, and construction use land drones for inspection and maintenance. These drones can inspect pipelines, infrastructure, and equipment in harsh environments where human inspection would be risky or impractical.
Land drones are making significant contributions to environmental monitoring and conservation efforts.
Land drones are used to monitor wildlife populations and their habitats. This non-intrusive method allows researchers to gather data on animal behavior, population dynamics, and habitat conditions without disturbing the animals.
Land drones equipped with various sensors can detect pollution levels in soil and water. They provide real-time data that helps environmental agencies in monitoring and mitigating pollution, ensuring a healthier environment.
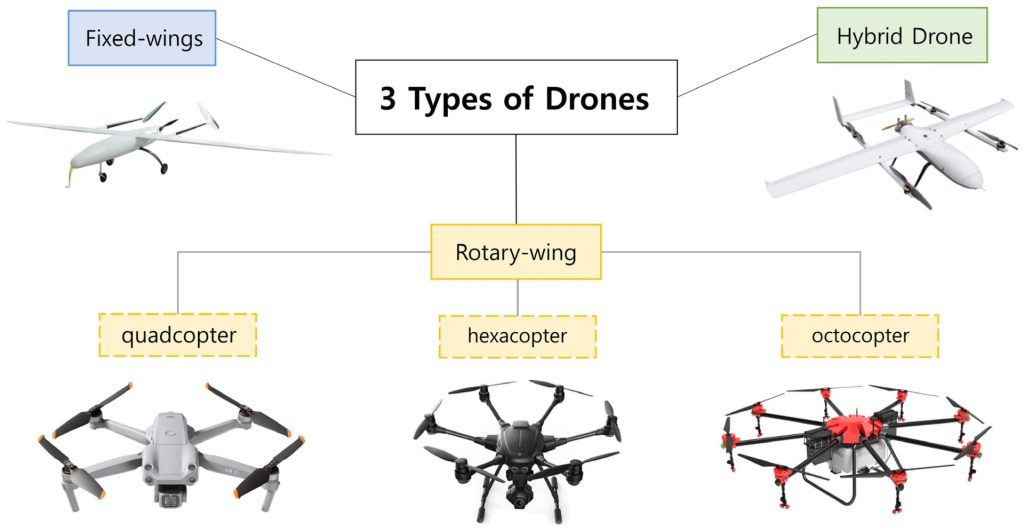
In healthcare, land drones are gradually finding their place, particularly in scenarios requiring safe and efficient delivery of medical supplies.
Land drones can quickly transport essential medical supplies, such as vaccines and medicines, to remote or inaccessible areas. This capability has been particularly useful in places with limited infrastructure or during pandemics when swift delivery is vital.
Land drones equipped with UV light or disinfectant sprayers are used in hospitals and public areas for sterilization purposes. They can navigate autonomously, ensuring large areas are disinfected thoroughly, reducing the risk of infection spread.
Security is another major area where land drones have found extensive use.
Equipped with cameras, sensors, and sometimes even deterrents like sirens or lights, land drones can autonomously patrol premises, providing constant security surveillance. They can cover large areas, detect intrusions, and alert security personnel in real-time.
Land drones are employed by law enforcement agencies for traffic monitoring and control. They can navigate through traffic, providing live data and helping in managing congestion and accidents more effectively.
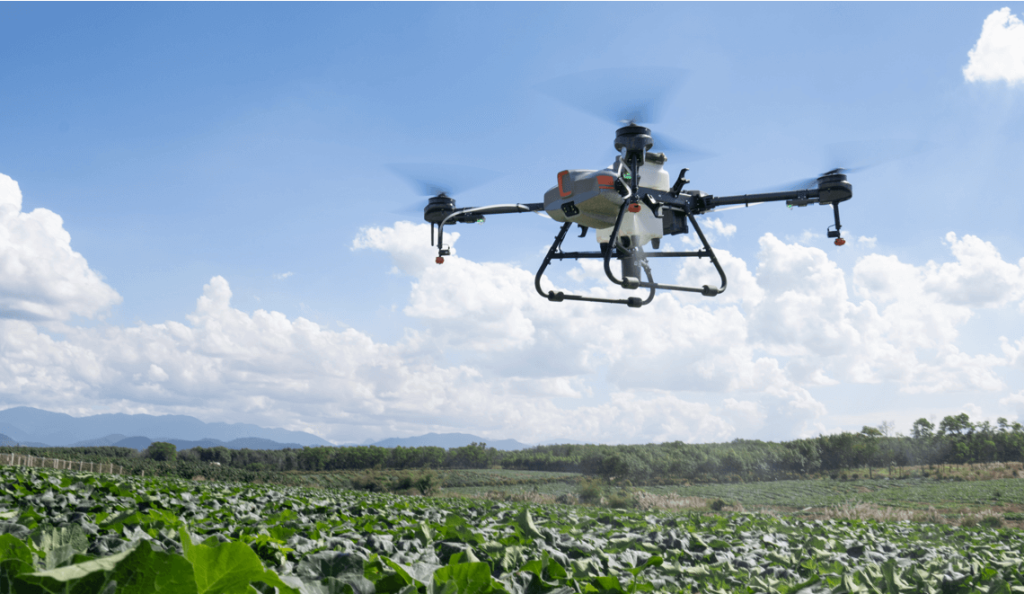

Academic institutions and research laboratories are utilizing land drones for a broad spectrum of research and educational purposes.
Land drones serve as platforms for testing new robotic technologies, including AI algorithms, navigation systems, and sensor integration. They enable researchers to validate their innovations under real-world conditions.
In educational settings, land drones are used to teach students about robotics, programming, and engineering principles. These practical experiences enhance learning and inspire the next generation of engineers and scientists.
The entertainment and media industry isn’t left behind when it comes to the innovative use of land drones.
Land drones equipped with high-resolution cameras are used in filmmaking and photography, enabling unique and dynamic shots that enhance storytelling. They can maneuver through tight spaces and capture angles that are challenging for traditional equipment.
In theme parks and entertainment venues, land drones are used to create interactive experiences for visitors. They can engage with people, offering features like games, informational tours, and more.
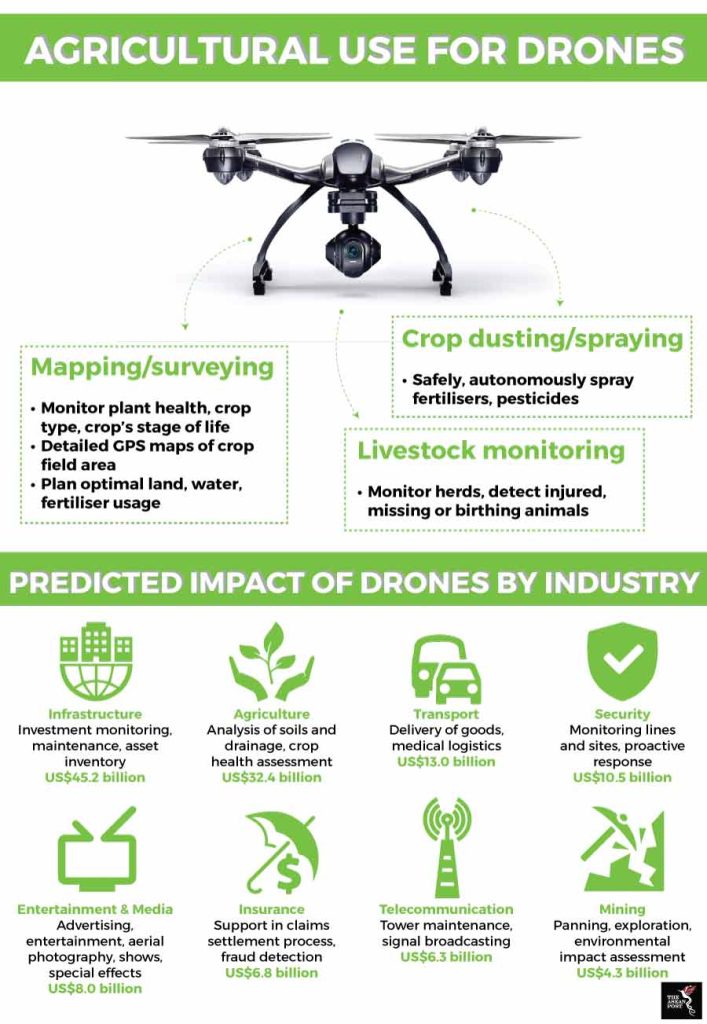
As technology becomes more accessible, land drones are making their way into homes and personal life.
Automatic vacuum cleaners and mopping robots are examples of land drones used for domestic cleaning tasks. They navigate through homes, cleaning floors autonomously and efficiently.
Land drones designed as robotic lawn mowers can maintain your garden by trimming grass to the desired length. They operate autonomously, saving you time and effort in lawn maintenance.
Land drones can be integrated into your home security system, patrolling your property and providing real-time surveillance, ensuring your home’s safety.
While the uses of land drones are impressive, there are challenges that need to be addressed for their wider adoption and improvement.
The operation of land drones involves navigating regulatory landscapes, as different regions have varying laws for unmanned vehicles. Clear and standardized regulations are necessary to ensure safe and legal drone operations.
While advanced, land drones still face technological limitations such as battery life, navigation in complex environments, and robust AI for autonomous decision-making. Ongoing research and development aim to overcome these challenges.
With the increasing use of land drones, ethical considerations around privacy, security, and employment arise. Balancing technological benefits with ethical implications is crucial for responsible deployment.
As you can see, the potential and existing uses of land drones are vast and impactful, spanning numerous sectors and solving diverse challenges. Their role is set to expand even further as technology continues to evolve, promising a future where many tasks are performed more efficiently, safely, and innovatively. Whether you’re a farmer monitoring your crops or a researcher studying wildlife, land drones offer powerful tools that revolutionize traditional methods and open new avenues for exploration and development.