Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, we may earn commissions from qualifying purchases.
Have you ever wondered about the small flying machines buzzing in the sky? These intriguing devices, known as aerial drones, have surged in popularity and functionality over the past years. Let’s embark on a friendly journey to uncover everything you need to know about aerial drones.
Aerial drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are aircraft without a human pilot on board. They are typically controlled remotely by a user on the ground or autonomously through pre-programmed flight plans.
Aerial drones have a fascinating history. Initially developed for military purposes, they have evolved into versatile tools used in various fields. Early drones were primitive compared to today’s advanced models, which boast sophisticated features like GPS, high-resolution cameras, and autopilot capabilities.
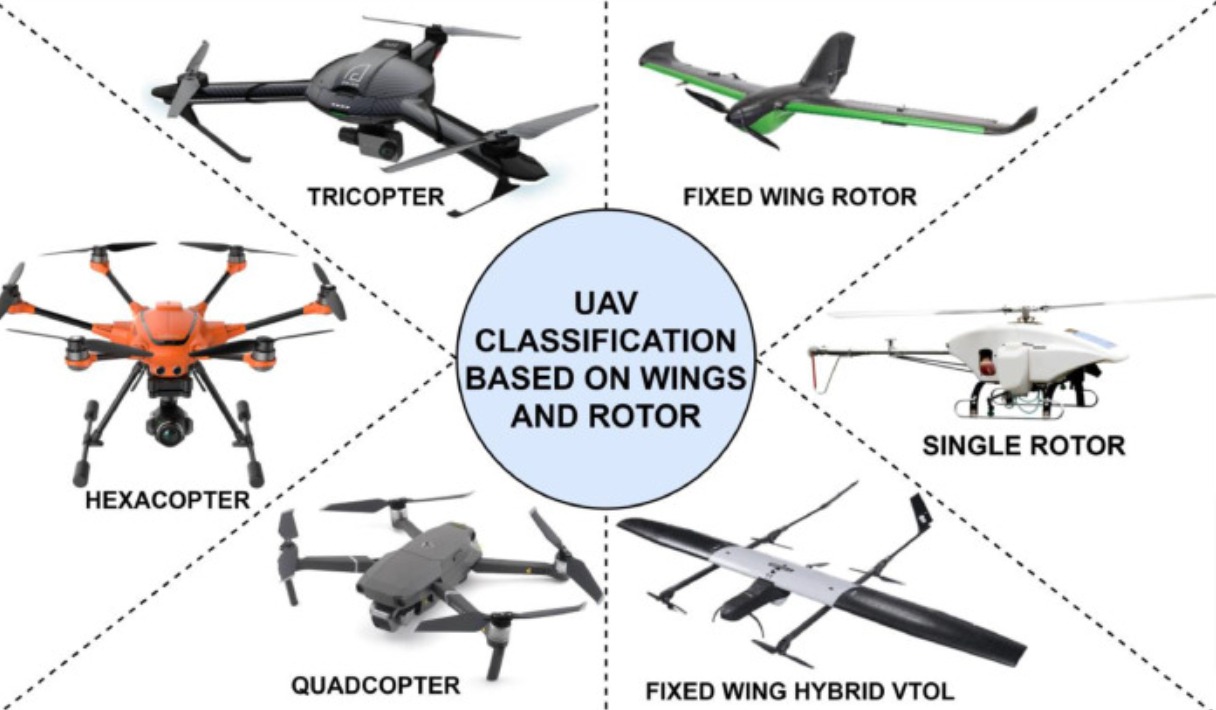
There are several types of aerial drones, each tailored for specific uses. They vary in size, functionality, and the technology they incorporate.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Multirotor | Commonly seen in civilian use, these drones have multiple rotors for stable flight and easy maneuverability. |
| Fixed-wing | Resembling traditional airplanes, they are known for their long flight endurance and are typically used for broader surveying tasks. |
| Single-rotor | Similar to helicopters with one large rotor and a tail rotor, they provide greater efficiency and longer flight times. |
| Hybrid VTOL | Combining features of multirotor and fixed-wing drones, these can take off and land vertically and transition to efficient forward flight. |
Understanding how aerial drones operate involves delving into their components and the technology that powers them.
Aerial drones consist of several fundamental components that work harmoniously to maintain flight and accomplish tasks.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | The structural body that holds all components together. |
| Propulsion System | Includes motors and propellers to generate lift and thrust. |
| Flight Controller | The brain of the drone, it manages orientation, speed, and stabilization. |
| Battery | Provides the necessary power to fly the drone. |
| GPS Module | Helps in navigation and positioning. |
| Camera | Used for capturing photos and videos or for FPV (First Person View) flying. |
| Sensors | Includes accelerometers, gyroscopes, and barometers to assist in stable flight and obstacle detection. |
| Receiver and Transmitter | Facilitates communication between the drone and the ground control system. |
When you control a drone, various mechanisms are at play to ensure stable and controlled flight. The motors and propellers provide the thrust needed to ascend, hover, and navigate. The flight controller processes sensor data to stabilize the drone, adjusting motor speeds as necessary. GPS modules aid in navigation, maintaining the drone’s position relative to waypoints or in enabling return-to-home functions.
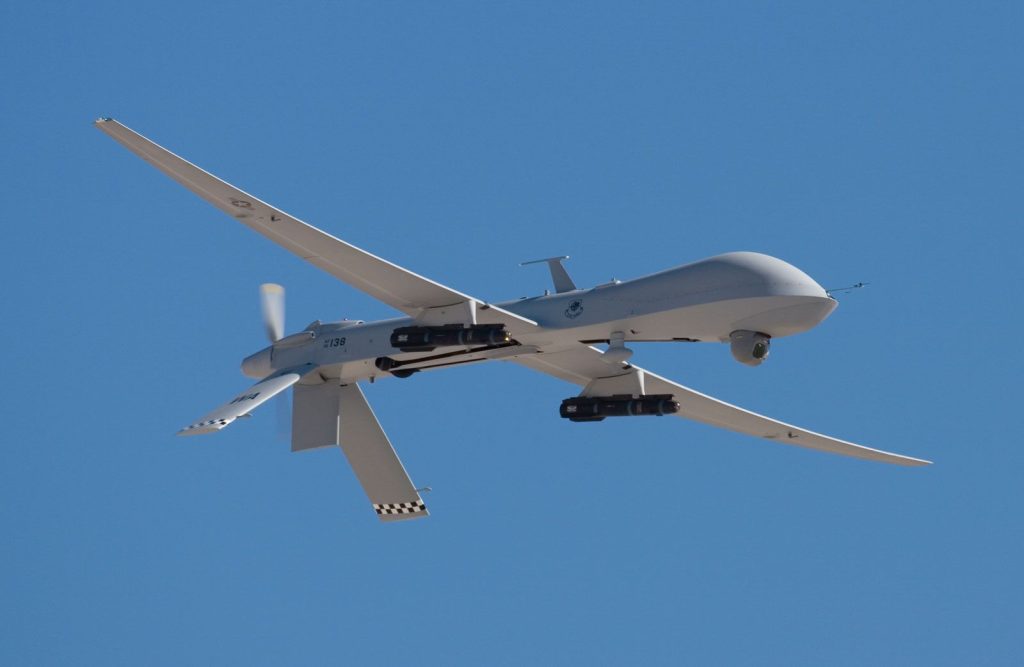

The versatility of aerial drones has led to their adoption across numerous sectors, each finding innovative ways to leverage this technology.
The military was the birthplace of drones, originally used for reconnaissance missions and targeted strikes. Modern military drones perform a myriad of functions, from surveillance to intelligence gathering, and in some cases, they participate in combat operations. Their ability to operate in dangerous environments without risking human lives is invaluable.
Drones have revolutionized precision agriculture, assisting farmers in monitoring crops, assessing field health, and even distributing pesticides. Equipped with multispectral sensors, drones can capture detailed images that reveal information about crop vigor, soil conditions, and irrigation needs. This data allows farmers to make informed decisions, optimizing their resources and increasing yields.
In emergency situations, drones can be deployed quickly to locate missing persons, assess disaster zones, and deliver critical supplies. Their ability to cover large areas swiftly and provide real-time aerial views is crucial in time-sensitive scenarios. Thermal imaging cameras on drones can detect body heat, making them invaluable in finding people trapped under debris or lost in challenging terrains.
Aerial drones have transformed the world of photography and filmmaking, allowing creators to capture stunning aerial shots that were once only possible with expensive helicopter rentals. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras can shoot from unique perspectives, adding a new dimension to visual storytelling.
Inspecting infrastructure like bridges, power lines, and wind turbines can be dangerous and costly. Drones offer a safer and more efficient alternative. Equipped with high-definition cameras and sensors, drones can get close to structures and provide detailed images for assessment. This helps in identifying potential issues early, preventing costly repairs and improving overall safety.
Drones play a significant role in environmental conservation efforts. They are employed to monitor wildlife populations, track deforestation, and assess the health of ecosystems. By collecting data from hard-to-reach areas, drones provide scientists with valuable insights that aid in preserving biodiversity and managing natural resources effectively.
The concept of drone deliveries is gaining traction, particularly in urban areas where traffic congestion can cause delays. Companies like Amazon and UPS are experimenting with drone technology to deliver packages rapidly and efficiently. While regulations and logistical challenges still need addressing, drone delivery holds promise for transforming logistics and supply chains.
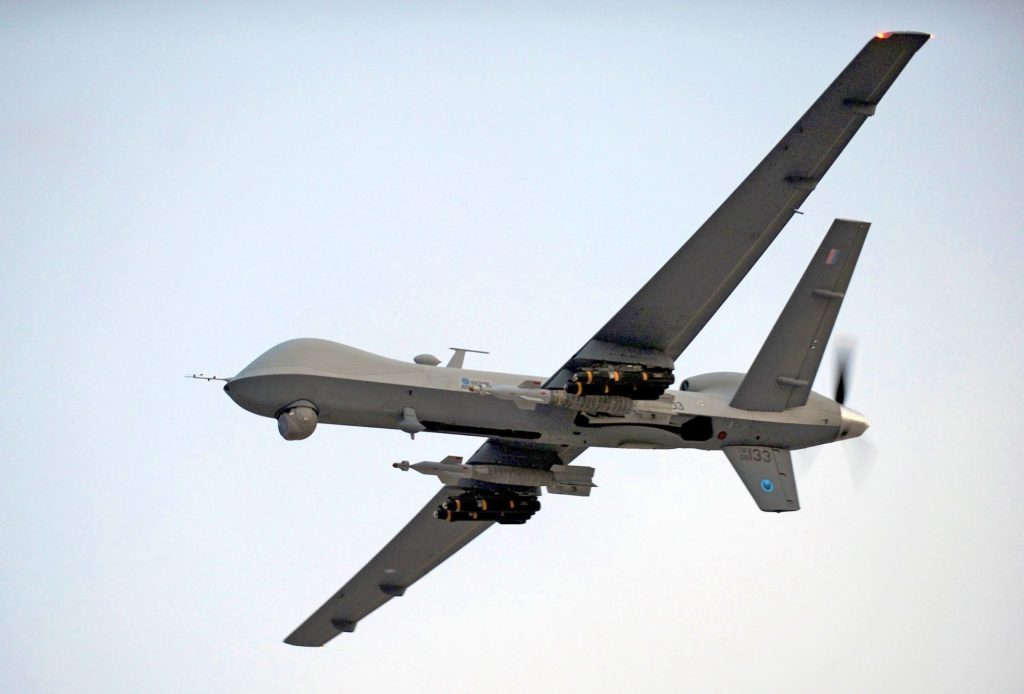

The proliferation of drones has led to the establishment of regulatory frameworks to ensure their safe and responsible use. Understanding these regulations is crucial for anyone operating a drone, whether for recreational or commercial purposes.
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) governs drone operations. Key regulations include:
Different countries have their own regulations regarding drone usage. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with the local laws if you plan to fly a drone internationally.
Drones equipped with cameras can potentially invade privacy. It’s important to respect people’s privacy by avoiding flying over private properties without permission and refraining from recording individuals without their consent.
Ensuring safe drone operation involves adhering to best practices. Always conduct pre-flight checks, avoid flying in adverse weather conditions, and maintain a safe distance from people, animals, and property. Regularly updating your drone’s firmware is also crucial for optimal performance and safety.

The future of aerial drones looks promising, with advancements in technology and new applications emerging constantly.
Integrating AI and machine learning into drones enhances their capabilities, allowing for more autonomous functions and smarter data analysis. Drones with AI can recognize objects, navigate complex environments, and make real-time decisions without human intervention. This opens up new possibilities in areas like autonomous delivery, environmental monitoring, and disaster response.
The concept of drone swarms involves multiple drones working together as a cohesive unit. This technology has the potential to revolutionize sectors like agriculture, where swarms can collectively monitor large fields, or in search and rescue operations, where they can cover vast areas rapidly. Swarms can also be employed in inspection tasks, offering multifaceted views of structures simultaneously.
Battery life remains a limitation for drones, but advancements in battery technology and alternative power sources promise longer flight times. Research into solar-powered drones and improvements in battery efficiency might soon enable drones to stay airborne for extended periods, enhancing their usability in various applications.
The rollout of 5G networks is expected to significantly impact drone technology. With faster data transmission and lower latency, 5G will enable more reliable connection and real-time communication between drones and their control systems. This could enhance the accuracy of drone navigation systems and facilitate complex operations like real-time video streaming for inspection or surveillance tasks.
As drone technology evolves, so do the rules governing their use. Future regulations will likely address emerging challenges and provide clearer frameworks to foster innovation while ensuring safety and privacy. Staying informed about these developments will be crucial for anyone operating drones professionally or recreationally.
The consumer drone market continues to grow, driven by decreasing costs and increasing accessibility. More individuals are discovering the joy of flying drones, leading to a rise in recreational drone pilots. As technology becomes more user-friendly and affordable, the adoption rate is expected to soar, further embedding drones into everyday life.

Aerial drones have come a long way since their inception, transforming industries and opening new horizons in technology and innovation. Whether you’re a hobbyist, a professional photographer, a farmer, or a tech enthusiast, the world of aerial drones offers something exciting for everyone. By staying informed about their capabilities, applications, and regulations, you can safely and effectively explore the boundless possibilities that drones bring to the sky.